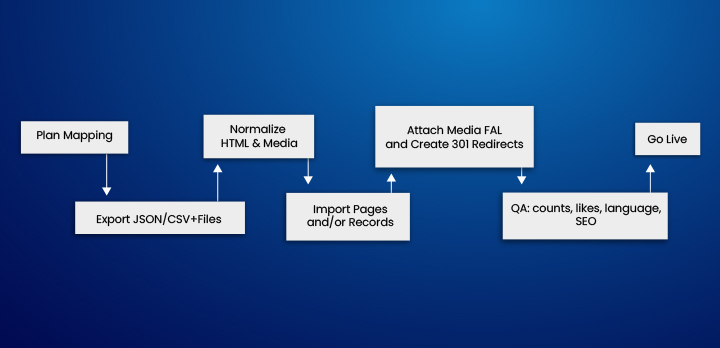
Control your data model and your URLs, and migration stays simple. This playbook gives a practical path from Drupal 11 to TYPO3 13, clean JSON/CSV exports, precise mappings, Twig→Fluid guidance, safe 301 redirects, and repeatable imports you can trust.
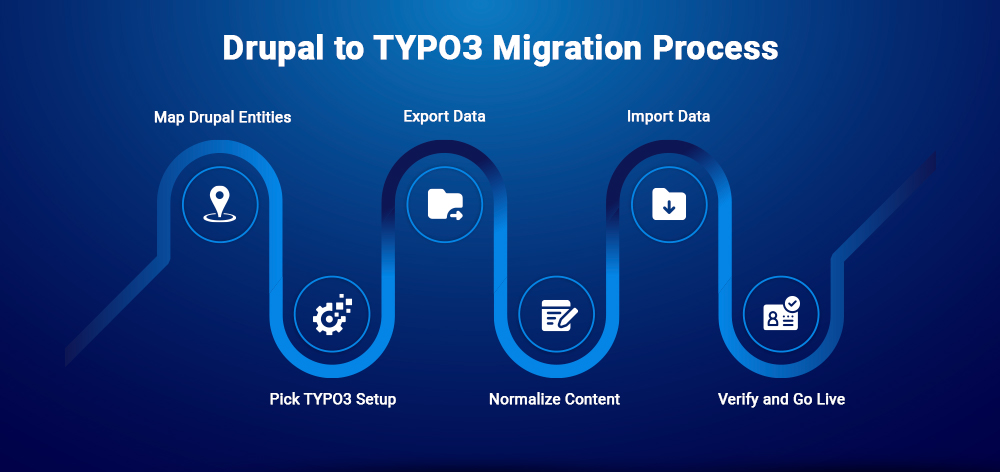
- Map Drupal entities → TYPO3 records and final slugs.
- Pick TYPO3 13 setup (Sites, languages, page tree).
- Export via JSON:API (or CSV via Views); copy files.
- Normalize HTML/assets; align templates (Twig→Fluid).
- Import categories, pages/records, media, and 301s.
- Verify counts, links, SEO; go live.
2) Minimal, Accurate Mapping
| Drupal | Example | TYPO3 Target | Notes |
| Node: Basic page | /about | Page + tt_content | Static content as text/image elements. |
| Node: Article/Blog | /blog/foo | Record (e.g., EXT:news) or Page | Prefer records for listings/filters. |
| Taxonomy term | “Events” | sys_category | Keep slugs; relate to pages/records. |
| User | Editors | be_users / be_groups (editors); fe_users / fe_groups (site users) | Separate back-office and front-office. |
| File | /sites/default/files/* | FAL (sys_file + sys_file_reference) | Keep filenames/folders for traceability. |
Understand Your Drupal Feature Requirements
Use migration to trim scope. Mark only what you truly need in TYPO3.
| Feature | Check | TYPO3 Capability |
| Personalization | ☐ | Via extensions/integrations |
| eCommerce | ☐ | ext:aimeos or ext:commerce |
| Multi-site | ☐ | Native Sites support |
| Roles/Permissions | ☐ | Granular BE/FE groups |
| Headless | ☐ | EXT:headless/custom APIs |
| Multilingual | ☐ | Native multi-language system |
| Workflow | ☐ | Workspaces (draft/review/versioning) |
| Media | ☐ | FAL with storages/metadata |
| Forms | ☐ | ext:form with editor |
| Accessibility | ☐ | WCAG-friendly output (templating) |
| CLI | ☐ | core and helhum/typo3-console |
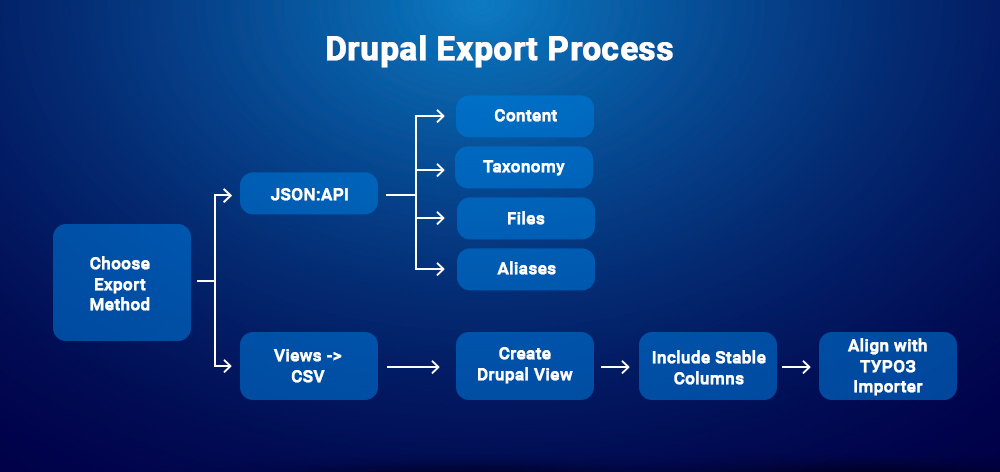
3) Export from Drupal (JSON or CSV)
A) JSON:API (recommended and repeatable)
- Content: /jsonapi/node/{bundle} (e.g., page, article)
- Use ?include=field_image,uid,field_tags to pull relations.
- Use ?page[limit]=N for pagination; export per language with filter[langcode]=….
- Taxonomy: /jsonapi/taxonomy_term/{vocabulary}
- Files: /jsonapi/file/file → use attributes.uri.url for the download URL.
- Aliases (for 301s): /jsonapi/path_alias/path_alias → keep source, alias, langcode.
B) Views → CSV (aligned to your importer in §6B)
- Create a Drupal View per entity (Pages, Articles, Categories, Users, Redirects, Files).
- Include stable columns: external_id (UUID), slugs, titles, HTML fields, dates, author email, category slugs, image URL(s), alias sources/targets.
- Keep column names consistent with your TYPO3 CSV importer to enable upserts and re-runs. (No code here—just the spec alignment.)
Role Mapping Snapshot
| Drupal Role | TYPO3 Equivalent |
| Administrator | Backend Admin User |
| Authenticated User | Frontend User (fe_users) |
| Anonymous | Anonymous Frontend access |
| Custom Roles | Custom BE/FE groups |
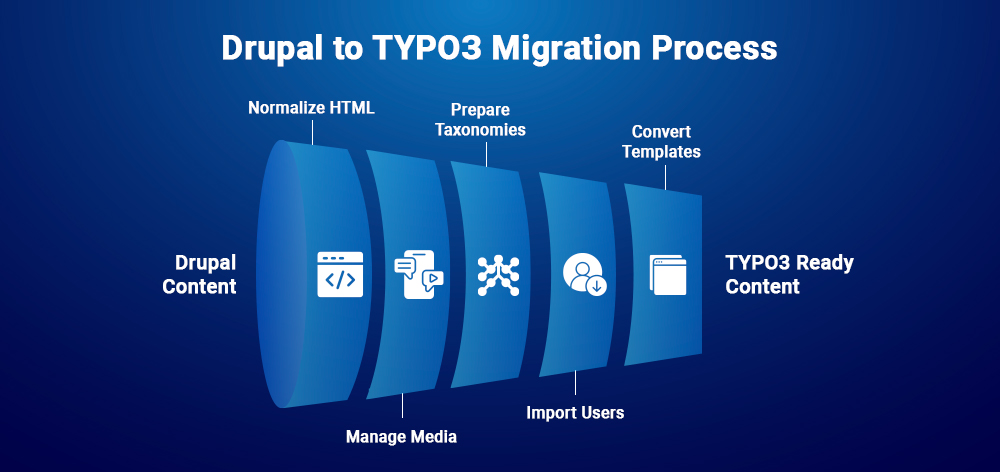
4–5) Normalize Content & Rebuild Templates (Twig → Fluid)
- HTML: Strip Drupal-specific filters; convert embeds to plain HTML or planned content elements.
- Media: Copy binaries to fileadmin/migrated/...; keep original filenames; prepare old-URL → new-path map.
- Taxonomies: Pre-create sys_category from export; reuse slugs where possible.
- Users: Import only needed editors/site users; map to BE/FE groups.
Drupal Twig → TYPO3 Fluid essentials
- Layouts/Partials: Twig {% include %} → Fluid <f:render partial="...">.
- Loops/Conditions: Twig {% for %} / {% if %} → Fluid <f:for> / <f:if>.
- URLs/Assets: Replace file_url() and hard paths with FAL-driven helpers and <f:uri.*> view helpers.
- Menus: Drupal menus → TYPO3 menu rendering from the page tree (TypoScript DataProcessors + Fluid).
- Translations: Keep language keys consistent; TYPO3 website languages must exist before importing translations.
{
"data": [{
"type": "node--article",
"id": "b5c1-uuid",
"attributes": {
"title": "My Article",
"body": { "value": "<p>HTML…</p>", "format": "basic_html" },
"created": "2025-05-01T10:20:30+00:00",
"langcode": "en",
"path": { "alias": "/blog/my-article" }
},
"relationships": {
"field_image": { "data": [{ "type": "file--file", "id": "f-uuid" }] },
"field_tags": { "data": [{ "type": "taxonomy_term--tags", "id": "t-uuid" }] }
}
}],
"included": [{
"type": "file--file",
"id": "f-uuid",
"attributes": {
"filename": "hero.jpg",
"uri": { "url": "https://example.com/sites/default/files/hero.jpg" }
}
}]
}Fetch & paginate (stage to disk)
function fetchDocuments(string $url): array {
$out = [];
while ($url) {
$json = json_decode(file_get_contents($url), true);
if (!is_array($json)) break;
$out[] = $json;
$url = $json['links']['next']['href'] ?? null; // JSON:API pagination
}
return $out;
}
// Example: articles with includes
$docs = fetchDocuments('https://drupal.example/jsonapi/node/article?filter[langcode]=en&include=field_image,uid,field_tags&page[limit]=50');
file_put_contents('stage/articles_en.json', json_encode($docs, JSON_PRETTY_PRINT|JSON_UNESCAPED_SLASHES));Import mapping (concept-level helpers; run inside TYPO3)
$docs = json_decode(file_get_contents('stage/articles_en.json'), true);
function indexIncluded(array $doc): array {
$files = $terms = [];
foreach (($doc['included'] ?? []) as $res) {
if ($res['type'] === 'file--file') {
$files[$res['id']] = [
'uuid' => $res['id'],
'filename' => $res['attributes']['filename'] ?? '',
'url' => $res['attributes']['uri']['url'] ?? null,
];
} elseif (str_starts_with($res['type'], 'taxonomy_term--')) {
$terms[$res['id']] = [
'uuid' => $res['id'],
'name' => $res['attributes']['name'] ?? '',
'slug' => $res['attributes']['path']['alias'] ?? null
];
}
}
return [$files, $terms];
}
foreach ($docs as $doc) {
[$fileIndex, $termIndex] = indexIncluded($doc);
foreach ($termIndex as $t) {
upsertCategory($t['uuid'], ['title' => $t['name'], 'slug' => $t['slug'] ?: slugify($t['name'])]);
}
foreach ($doc['data'] as $node) {
if ($node['type'] !== 'node--article') continue;
$uuid = $node['id'];
$attr = $node['attributes'];
$rels = $node['relationships'] ?? [];
$title = $attr['title'] ?? '';
$body = $attr['body']['value'] ?? '';
$lang = $attr['langcode'] ?? 'en';
$alias = $attr['path']['alias'] ?? null;
$slug = $alias ?: '/'.slugify($title);
$pageUid = upsertPage($uuid, [
'pid' => 0,
'title' => $title,
'slug' => $slug,
'sys_language_uid' => langUid($lang),
]);
insertTextElement($pageUid, normalizeHtml($body), $title);
foreach ((array)($rels['field_image']['data'] ?? []) as $imgRef) {
$fileMeta = $fileIndex[$imgRef['id']] ?? null;
if (!$fileMeta || empty($fileMeta['url'])) continue;
$fileUid = ensureFalFromUrl($fileMeta['url'], $fileMeta['filename']);
attachImageToPage($pageUid, $fileUid);
}
foreach ((array)($rels['field_tags']['data'] ?? []) as $ref) {
relatePageToCategory($pageUid, externalIdToCategoryUid($ref['id']));
}
if ($alias) rememberRedirect($alias, $slug, 301);
}
}
flushRememberedRedirects();
/* Helper signatures you’ll implement with TYPO3 APIs (DataHandler + FAL):
upsertCategory($externalId, $data): int
upsertPage($externalId, $data): int
insertTextElement($pid, $html, $header): int
ensureFalFromUrl($url, $filename): int
attachImageToPage($pageUid, $fileUid): void
relatePageToCategory($pageUid, $categoryUid): void
externalIdToCategoryUid($externalId): ?int
langUid($langcode): int
slugify($text): string
normalizeHtml($html): string
rememberRedirect($source, $target, $status): void
flushRememberedRedirects(): void
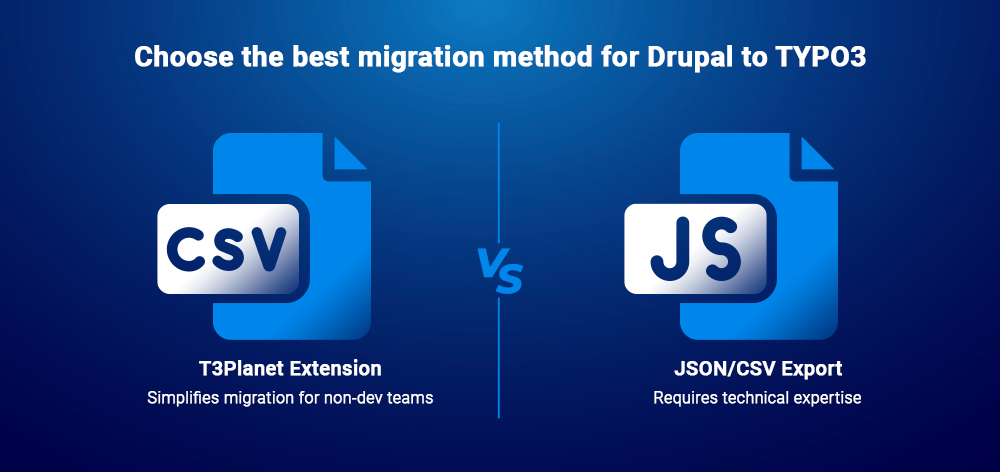
*/If you can export Drupal into CSVs similar to the WordPress schema used by T3Planet’s “Migrate WordPress to TYPO3” extension, you can use that tool for Drupal, too. It’s ideal for non-dev teams and repeatable dry runs.
Map Features to TYPO3 Extensions (practical set)
| Drupal Feature | TYPO3 Extension | Key |
| News/Blog | News System | ext:news |
| SEO (meta/sitemap) | On-page SEO | ext:seo (core) |
| Forms | Form Framework | ext:form |
| Newsletter | Direct Mail / integrations | ext:direct_mail |
| eCommerce | Aimeos | ext:aimeos |
| Workflow | Workspaces | Core |
| Drush-like CLI | TYPO3 Console | Core helhum/typo3-console |
Wrap-up
Keep it predictable: stable UUIDs, clean JSON/CSV, FAL for media, and 301s for every alias. Decide early on records vs. pages, mirror category slugs, and run imports idempotently until the diff is zero. Then ship.
FAQ
Yes. Export via JSON:API or CSV, copy files, import into TYPO3 13, and preserve URLs with 301s.
Store Drupal UUIDs as external_id in TYPO3 and upsert on that key. Re-runs update rather than duplicate.
Use records (e.g., EXT:news or a custom TCA) for high volume, filtering, and feeds. Keep static content as pages.
Recreate final slugs in TYPO3 and import Drupal aliases into sys_redirect as 301s. Validate top URLs, language variants, and avoid redirect chains.
Copy binaries, register each file in FAL (sys_file + metadata), and attach via sys_file_reference. Keep original filenames/folders for auditing.
Yes. Export CSVs via Drupal Views and use the T3Planet migration extension. It’s easy to audit and repeat.
Rebuild in Fluid: map Twig blocks/partials to Fluid layouts/partials and use FAL + <f:uri.*> helpers for URLs/assets.







Wolfgang Weber
Brand & Communication LeadWolfgang Weber shapes TYPO3 with passion and expertise. As TYPO3 enthusiast, he has contributed to TYPO3 projects that make websites faster and more secure. Outside of TYPO3, you'll probably find him exploring local cafés and…
More From Author